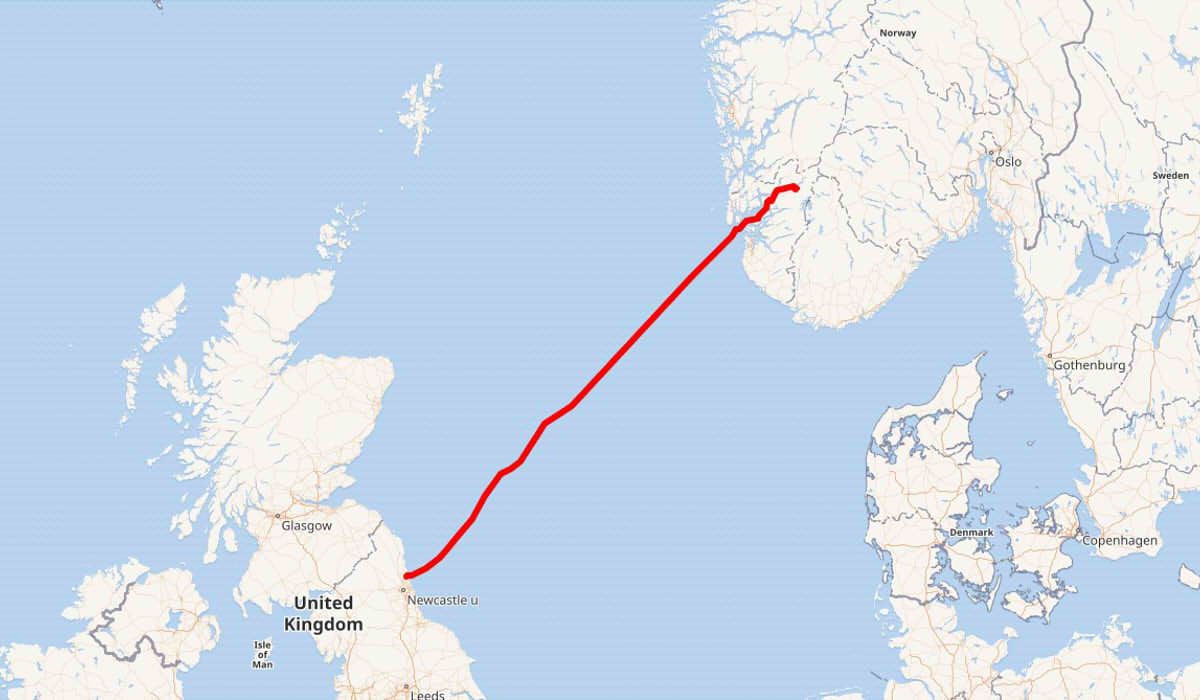
The North SeaLink high-voltage submarine cable (NSL) connecting the United Kingdom and Norway with a capacity of 1400MW, the 13 of June, after suffering a decrease in its operating capacity due to a technical failure.
North Sea Link (NSL) is a ±525kV flexible direct current transmission project that connects the power systems of both countries through a submarine cable of 720 km long, whose construction was completed in early June 2021. The 18 of June, the first test was carried out, with the cable running from the Kvilldal power station in Norway to the port of Blyth in the United Kingdom. This project, valued at 1.600 millions of euros, was put into operation 1 October 2021.
Several months ago, The Statnett company decided to reduce the maximum capacity of the cable to 1400MW to balance the loads at both ends.
Nevertheless, the 8 June 2023, Statnett reported that a failure in the rectification system caused a cable breakdown, leaving the NSL connector inoperative. The high-voltage submarine cable temporarily operated with a capacity of 700MW until repairs were completed. Today, The fault has been repaired and the cable is working at full capacity again..
Why Use DC Technology for Submarine Cables?
The use of direct current technology in underwater electrical cables It is mainly due to the need to reduce losses in long distance transmission. In the case of submarine cables, being surrounded by sea water, capacitance is high during long distance transmission. If alternating current were used, high capacitance could cause deviations or even the inability to deliver power. Besides, alternating current generates varying magnetic fields around conductors, resulting in significant energy loss.

What to Do If the Submarine Cable Fails?
In the event of a failure in a submarine cable, It is a serious problem that can cause great losses. An example of this occurred on 24 June 2017, when the container ship MSC Alice, docked in front of the port of Mogadishu in Somalia, accidentally cut an underwater fiber optic cable, causing an internet blackout in Somalia for more than half a month. Since the beginning of the interruption, The daily economic loss in the region reached 10 millions of dollars, with a total loss of more than 150 millions of dollars.
As mentioned earlier, Failures in submarine cables are a very serious problem that can result in significant losses. So, How is a submarine cable repaired in case of a failure?
Currently, Submarine cable failures generally fall into two categories. The first is external damage, What happens when cables are damaged by the anchors of boats or fishing vessels that snag them, resulting in damage to the exterior of the cable. The second type of failure is the aging of the internal insulation of the cable, namely, internal failures that occur due to cable wear itself.
Two types of insulation for HVDC submarine cables
According to the main insulation method used in HVDV submarine cables, can be divided into two main categories: rolled type and extruded type.
The HVDV coiled paper and oil insulation submarine cable was the first to be used in high voltage direct current submarine transmission projects.. Depending on the insulating medium, This type of insulation cable is classified into two types: dripless oil immersed cable (MIND) Y insulation wire laminated paper polypropylene (PPLP).
MIND cable uses oil-immersed insulating paper, while PPLP cable uses polypropylene laminated insulation paper. Because they both use paper insulation, the operating temperature of submarine cables cannot be too high.

Secondly, Submarine cables with extruded insulation began to be used in the 1990s. 1990. This technique has significant advantages compared to the rolling technique.: they are lighter, easier to maintain and can operate at high temperatures.
Direct current extruded insulation submarine cables can be classified into two types according to the insulating material.: cross-linked polyethylene cables (XLPE) and thermoplastic elastomer cables (HPTE).
Currently, High voltage submarine cables continue to expand towards high voltage and high capacity. Currently, technology has enabled PPLP insulated cables to achieve voltages of ±800 kV and transmission capacity of up to 4000 MW. Los XLPE insulated cables can reach voltages of ±600 kV and a transmission capacity of up to 3000 MW.
Repair of faults in submarine cables
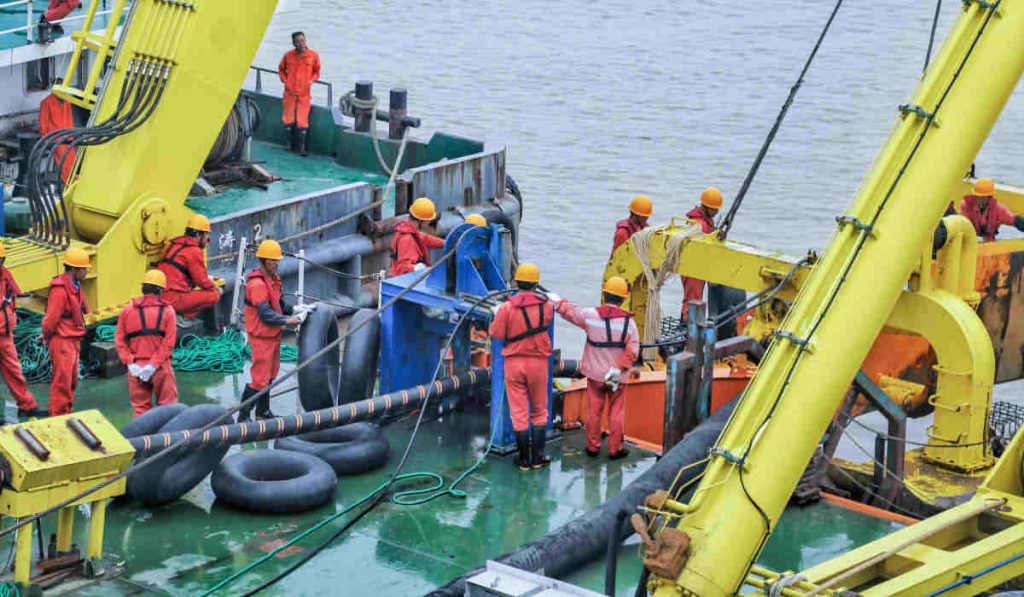
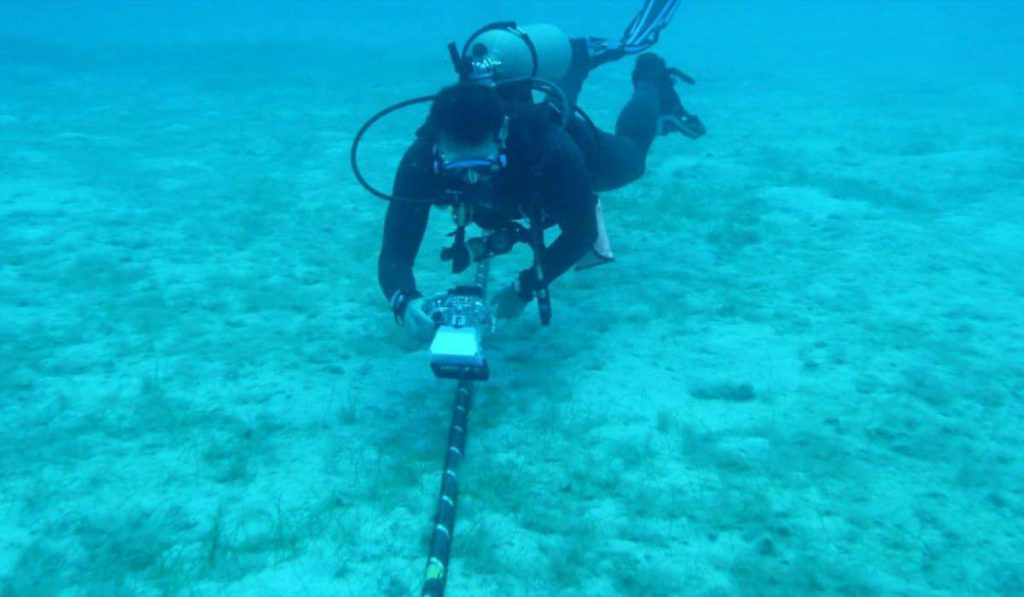
Usually, after an undersea cable is damaged, the use of specialized equipment is required to detect its location and possible problems. Once the failure point is confirmed, Divers can be sent to carry out repairs on the seabed or recover the damaged section on board the ship for repair.

After rescuing the high-tension submarine cable and bringing it on board, Technicians are needed to perform procedures such as cutting, dehydration, preparation of splices and sealing with lead to ensure tightness and dryness of the cable. Once the preparation of the splices is completed, Insulation and resistance tests are carried out to verify the safety and reliability of the cable section.
To ensure faster localization and timely correction of errors, It is essential to be up to date with the latest technologies. For example, Currently, underwater robots have been developed that, through advanced autonomous control systems and high-precision mechanical arms, can automatically locate cable faults and carry out necessary repairs.
The Future of High Voltage Submarine Cables
With increasing demand for regional power grid interconnection and the development of offshore wind energy, los underwater direct current cables are moving towards higher voltages, Greater capacity and greater distances.
The main technical challenges facing submarine DC cables today are the electrical and thermodynamic performance of insulation materials., cable structure design, accessory reliability and fault location technology.
With the continued increase in submarine cable projects globally, The establishment of more specialized submarine cable construction and maintenance teams will become one of the main future requirements.