At the core of the modern military, military cables play a critical role. They are the arteries and nerves that transmit electrical energy and the information necessary for the operation of weapons and military equipment.. This article will delve into the historical evolution of military cables and their role in submarines., missiles and fighter planes.

Historical Origins of Cables
Cables have roots in pioneering scientific experiments, such as Benjamin Franklin's famous kite experiment in which he demonstrated the connection between electricity and lightning. Franklin used a long iron rod with a metal cable to attract lightning and protect buildings. It is metal cable It is considered the precursor of modern cables.
Over time, cable technology evolved, and today there are numerous types of military cables designed for different applications in defense and construction..
Identification by Color: The Clothing of the Cables
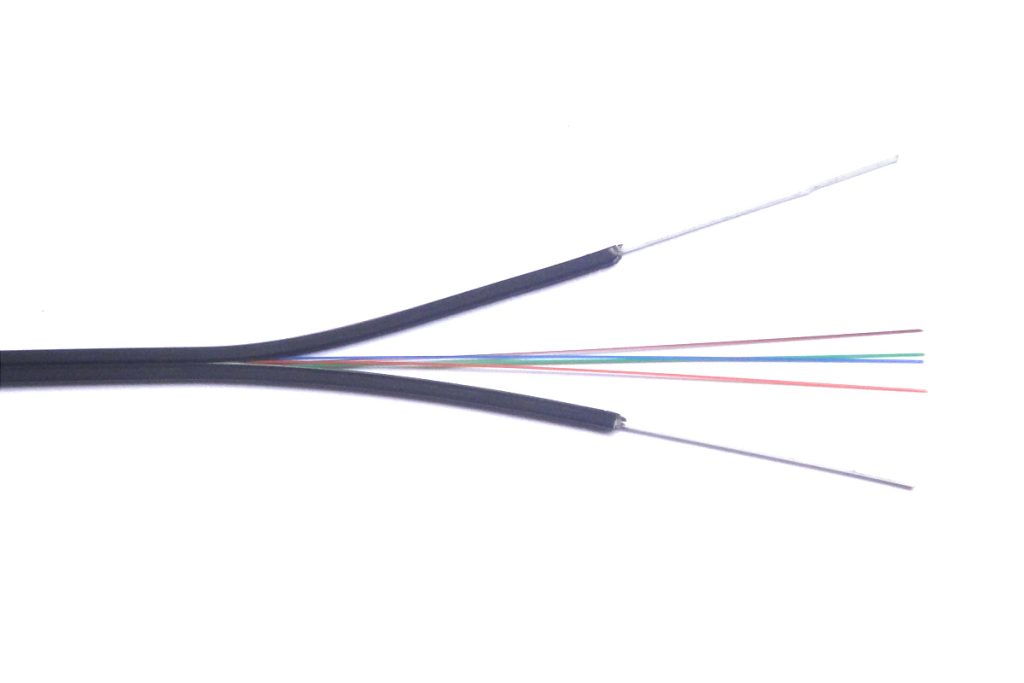
Military cables come in a variety of types, and its identification is based on specific colors, following strict national and military regulations. Colors, like yellow, verde, rojo, light blue and others, indicate the type of cable and facilitate quick identification in the field.
For example, yellow can indicate a high voltage cable, while red can indicate a safety cable. This color coding is essential to ensure safety and precision in cable management in military environments..
Delicacy in Thinness: Fiber Optic Cables
Some military cables are surprisingly thin. copper cables, with a diameter of approximately 0.035 mm, They are common and slightly thicker than a human hair. Nevertheless, Fiber optic cables are even thinner and can transmit signals equivalent to thousands of copper cables. These fiber optic cables are essential in technologies such as 5G.
In 2017, A research group set a world record by developing a nanowire with a diameter equivalent to just three stacked atoms.. Although the thinness is impressive, not always the best option, since current carrying capacity and resistance are important.
The Balance between Thickness and Thinness
The thickness of a cable military is crucial and varies by application. Medium and long range missiles, like the Russian Sarmat, require cables the thickness of a man's thigh to support the necessary electrical load. In missile manufacturing, every gram counts, since a lighter missile has greater mobility. Consequently, Finding the perfect balance between thickness and thinness is a fundamental technical challenge.
Thicker cables can carry higher electrical currents, which is essential for powerful weapons such as intercontinental missiles. Besides, These thick cables can withstand extreme conditions, such as the vibrations and shocks that missiles experience during their launch and flight.
The Conquest of the Oceans: Submarine Cables
The importance of military cables extends beyond land. The installation of the first transatlantic submarine cable in 1858 by Cyrus Westfield was a landmark. This cable allowed faster and more efficient communication between Europe and the United States, marking a quantum leap in the transmission of information worldwide.
Military submarine cables play a vitally important role in military communications infrastructure by ensuring the secure and reliable transmission of strategic and tactical information in underwater environments.. These cables are essential for the coordination of military operations, the transmission of intelligence data and communication between submarines and land bases.
Its design and construction are carried out with a meticulous focus on water and humidity resistance, ensuring they remain operational in the abysmal depths of the ocean, where any disruption in communication could have critical consequences for national security.
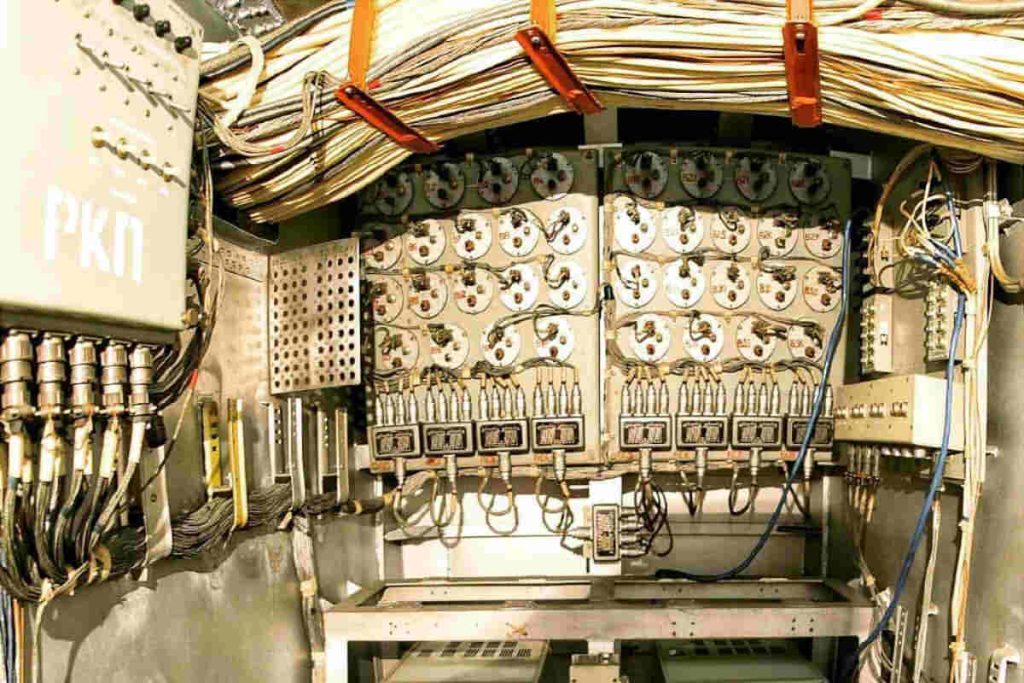
The Silent Heroes: Cables in Submarines
The submarine force, often called the “silent army”, depends on highly flame retardant cables and watertight. These cables guarantee the integrity of electrical connections in an underwater environment, where a short circuit could be catastrophic.
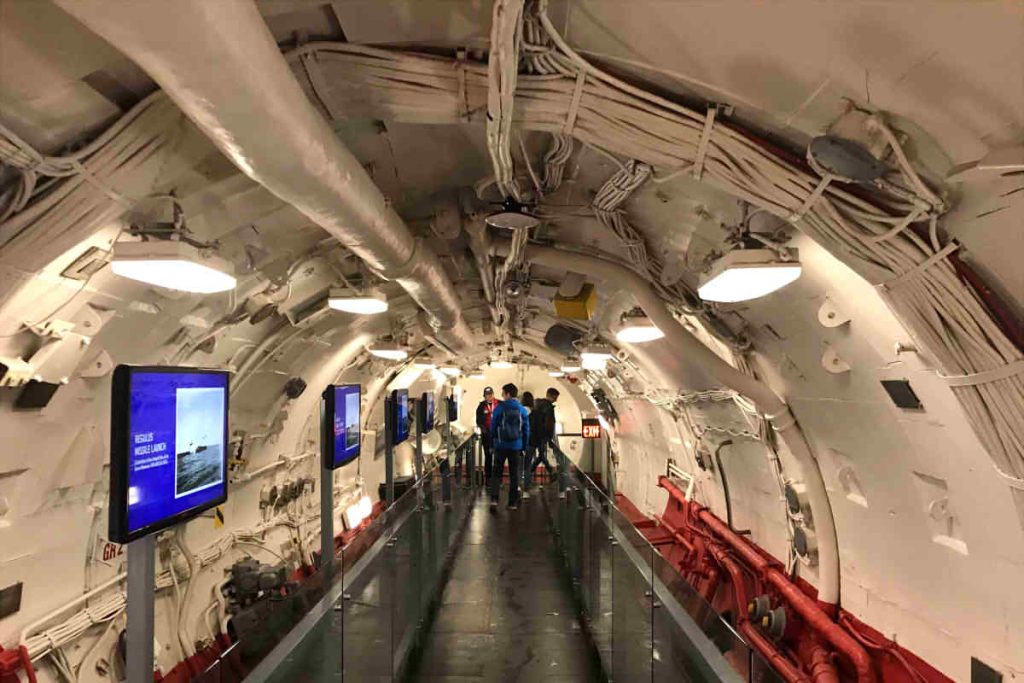

To ensure safety, These cables are often insulated with special materials that can withstand high temperatures and maintain their integrity in the event of a fire.. The reliability of these cables is essential for the safe operation of submarines, who often dive to extreme depths and face hostile conditions.
The Cable Network in Missiles
Missiles have specific requirements for the cables that make them up. Cable layout on missiles is highly integrated. Los “in-pump cables” of a missile connect a series of critical components, meaning a single missile can contain thousands of cables. Durability and the ability to withstand extreme conditions are essential to ensure a missile functions properly.
These cables must be resistant to the heat generated by the missile's engine and able to withstand vibrations and shocks during launch and flight.. Besides, They must be flexible enough to accommodate the compact internal structure of a missile.
Cables in Fighter Aircraft
Fighter planes use air-to-air missiles that depend on cables specially designed to withstand high and low temperatures, low pressure at high altitudes, vibrations and shocks. These cables must be strong and light., since every gram counts in military aviation.
The engineering behind these cables is impressive, since they must withstand the extreme conditions of aerial flight and guarantee the electrical connectivity essential for the operation of weapon systems.
Conclusion
In the modern world of defense, Military cables are the backbone of communication and electrical energy. From its humble origins in Franklin's experiments to today's ultra-thin and ultra-thick cables, These essential components play a critical role in the safety and efficiency of armed forces around the world.. Its evolution continues as the demands of modern warfare require greater mobility., flexibility and responsiveness in military systems.

