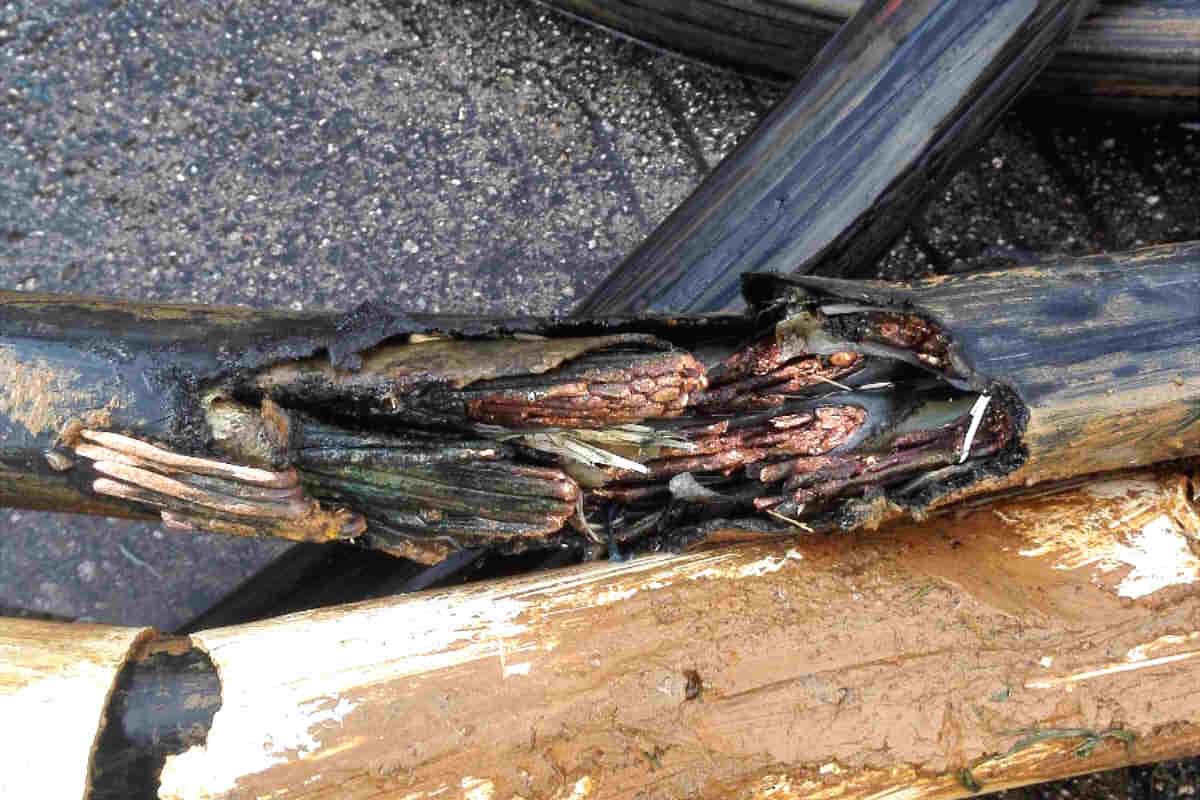
The principle of corrosion of copper cables and aluminum cables refers to a chemical process that occurs when these cables come into contact with the specific environment, causing rust and damage to the metal surface. These chemical processes mainly include two mechanisms: electrochemical corrosion and chemical corrosion.

Table of Contents
Types of Corrosion in Cables
Electrochemical corrosion
Electrochemical corrosion occurs when metals react with ions in an electrolyte solution, generating electric current that causes oxidation and damage to the metal surface.
In the case of the metal electrical cables like copper and aluminum, They act as anodes (most active metals) in the presence of water and air, while oxygen ions in water and air function as cathodes. In these conditions, An oxide layer forms on the surface of copper and aluminum cables.
Due to the low conductivity of this oxide layer, metal ions at the anode release electrons, flowing through the electrolyte solution towards the cathode, where they combine with oxygen ions to form oxides.
Besides, The metal ions at the anode also react with other elements in the water, as aluminum ions react with hydroxyl ions to form aluminum hydroxide precipitates. These reactions gradually cause corrosion and deterioration of the copper and aluminum surface..
chemical corrosion
Chemical corrosion occurs when metals react directly with specific chemicals, resulting in oxidation and damage of the metal surface.
Both the copper core cables as aluminum ones can react with certain chemicals, what causes corrosion. For example, Copper cables are susceptible to chemical corrosion by sulfur compounds such as sulfur dioxide and hydrogen sulfide..
Copper ions on the surface of wires can react with sulfur dioxide, producing substances such as copper sulfate and copper thiosulfate, leading to corrosion and color change on the surface of the copper wire.
Similarly, aluminum cables can be affected by strong oxidizing agents, such as oxygen in acid solutions and chlorine. The oxide film on the surface of aluminum cables can be destroyed by oxygen or chlorine. This exposes the metal and causes oxidation reactions., resulting in corrosion and damage to aluminum cables.
Factors Affecting Corrosion
In addition to the electrochemical corrosion and chemical corrosion mentioned above, Copper and aluminum cables can also be influenced by other factors that intensify the corrosion process., as:
Temperature
The increase in temperature accelerates the oxidation and corrosion process of metals. In high temperature environments, metal ions have a greater propensity to react with ions in solution, resulting in faster corrosion rate.
Humidity

High humidity environments increase contact between metals and water vapor, accelerating oxidation and corrosion. In environments with high humidity, the oxide film on the metal surface attracts more moisture, forming a electrolytic layer which facilitates the transfer of electrons and, consequently, accelerates the corrosion reaction.
pH
The pH of the solution also affects the corrosion rate of metals.. In acidic solutions with a low pH, the oxide film on the metal surface dissolves more easily, which intensifies corrosion.
Corrosion Prevention Measures
To protect copper and aluminum cables, which are widely used in various industrial and domestic applications, Various prevention strategies are implemented. These strategies are essential to extend the life of cables and ensure their efficient operation..
Electroplating Protection
Electroplating is an effective technique to protect copper and aluminum cables. It consists of applying a thin metallic coating on the surface of these conductors for cables. Commonly used materials for cladding include:
- Tin: Provides excellent corrosion protection and improves solderability of cables.
- Plata: Although more expensive, Silver offers exceptional corrosion resistance and better electrical conductivity.
- Zinc: It is an economical material that provides good protection by sacrificing itself in place of the base metal..

Anodic Protection
Anodic protection is an approach that uses the sacrificial nature of certain metals to protect copper and aluminum cables.. This technique involves:
- Install anodes made of more active metals, like zinc, in proximity to cables.
- These anodes preferentially corrode, sacrificing themselves and therefore protect copper and aluminum.
- It is a technique widely used in marine environments and in situations where cables are exposed to severe corrosive elements..
Coating Protection
Sheathing is one of the most direct and versatile ways to protect cables. This method includes:
- Apply a layer of corrosion resistant material, such as special paints or plastic coverings for cables.
- These coatings act as a physical barrier, preventing corrosive environmental factors from coming into direct contact with the metal.
- The coatings can be of various types, from epoxy paints to thermoplastic polymers, depending on exposure conditions and specific requirements.
Implementing these measures, copper and aluminum cables can maintain their integrity and functionality over time, avoiding premature failure and costly repairs or replacements. These strategies are crucial in industries where cable reliability and durability are critical., as in telecommunications, building, and electrical networks.
Conclusion
In summary, Corrosion of copper and aluminum cables is mainly due to chemical reactions with the surrounding media, leading to rust and damage to the metal surface. Understanding the principles of corrosion is crucial to taking preventive measures and extending the life of copper and aluminum cables..

