optical fibers, Known for their ability to transmit data at incredible speeds with minimal loss, have revolutionized the way information is shared globally. Nevertheless, many people are not as aware of the cost and materials of optical fibers as they are of metal conductor cable. This article aims to delve deeper into the intricate components that determine the fiber optic price..
Table of Contents
- Fiber Optic Price Reference
- Composition and Manufacturing of Optical Fibers
- Material Costs and Price Fluctuations
- Fiber Optic Communication Equipment Prices
- Example: Cost and Profitability Analysis for a Communication Service Provider
- Conclusion
Fiber Optic Price Reference
The cost of fiber optics is influenced by several factors, including raw material prices, manufacturing processes, market demand and global economic conditions. These elements collectively determine the unit price of fiber optics, which can range from tens to hundreds of dollars per kilometer, depending on the type, quality and application. Next, Some common types of fiber optics and their approximate price ranges are presented in 2024 (Please note that these prices are subject to market fluctuations):
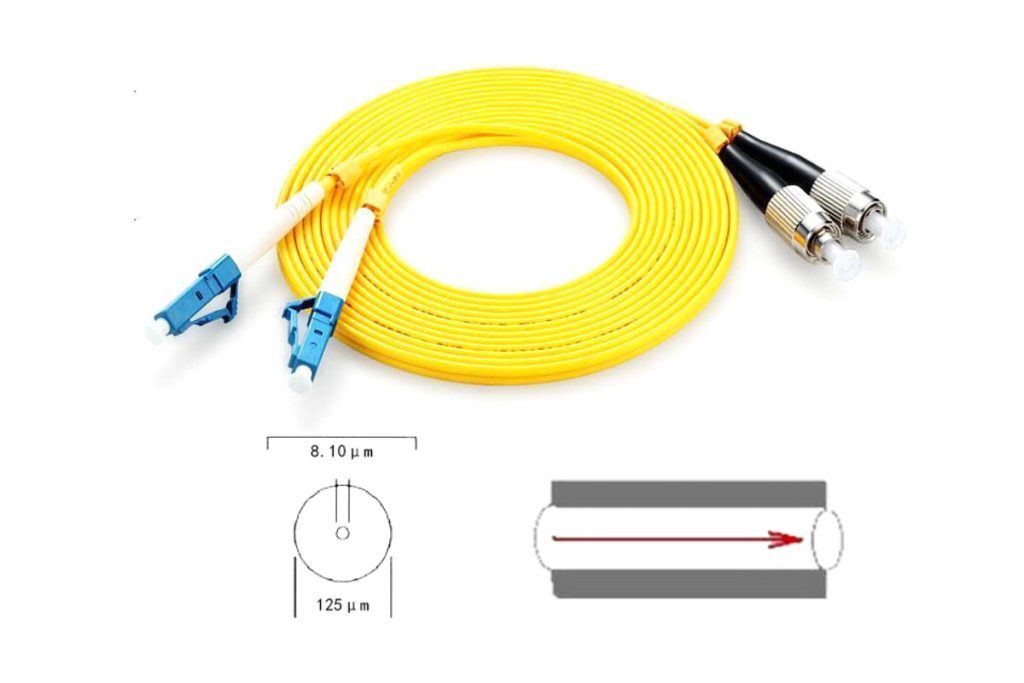
1.Singlemode Fiber:
- Typically used for long distance transmissions and high speed communication networks.
- Price range: about $0.30 a $1.50 per meter, o $300 a $1,500 per kilometer.

2.Multimode Fiber:
- Mainly used in local area networks (LAN) and short distance communications.
- Price range: about $0.20 a $1.00 per meter, o $200 a $1,000 per kilometer.
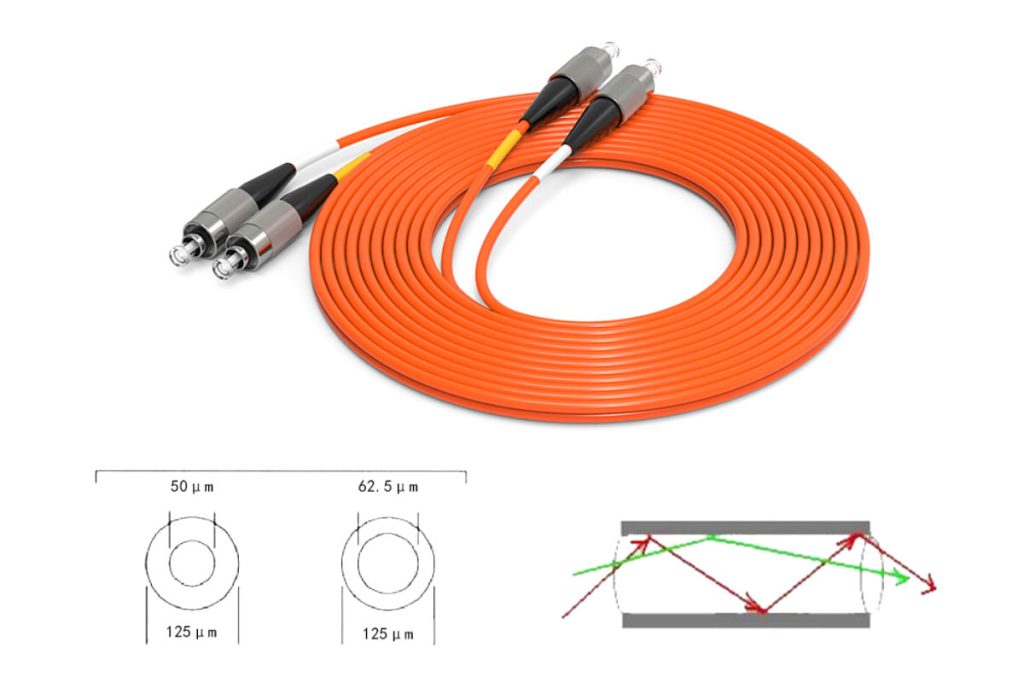
Learn more: Complete Introduction to Multimode and Singlemode Fiber
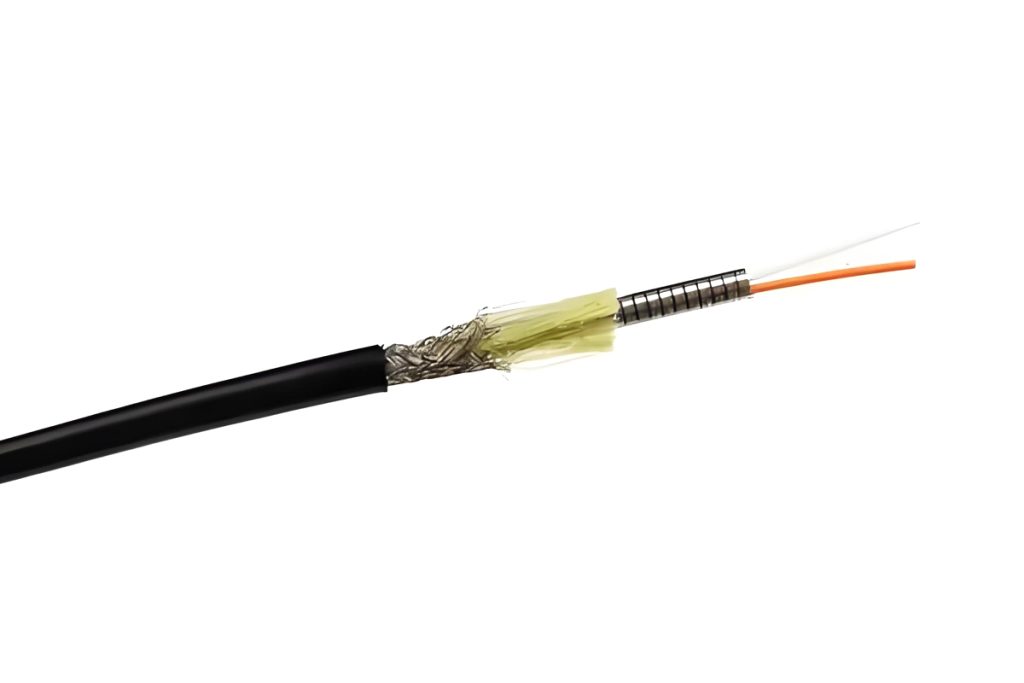
3.Armored Fiber Optic Cable:
- This type of fiber optic armored cable is designed for enhanced protection in harsh environments, often used in industrial settings.
- Price range: about $1.00 a $5.00 per meter, o $1,000 a $5,000 per kilometer.

4.Total Dielectric Self-Supported Fiber Optic (ADSS):
- Used for aerial installations without the need for metal support, ideal for electrical service environments.
- Price range: about $2.00 a $10.00 per meter, o $2,000 a $10,000 per kilometer.
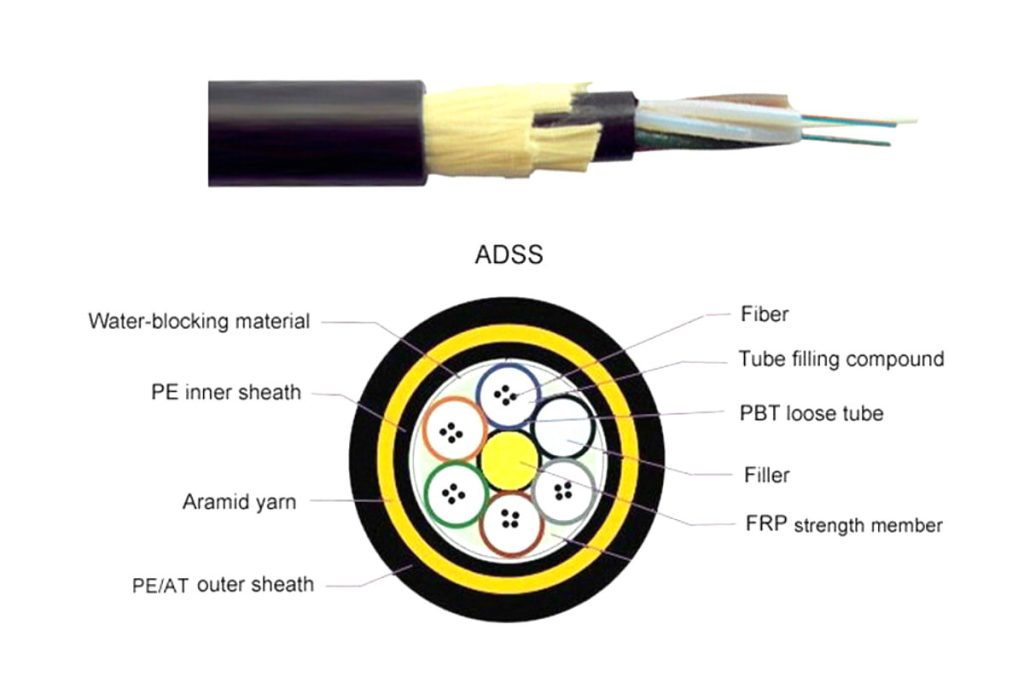
5.Fiber Optic with Ground Cable (OPGW):
- Integrated into power transmission lines for both grounding and communications.
- Price range: about $3.00 a $30.00 per meter, o $3,000 a $30,000 per kilometer.
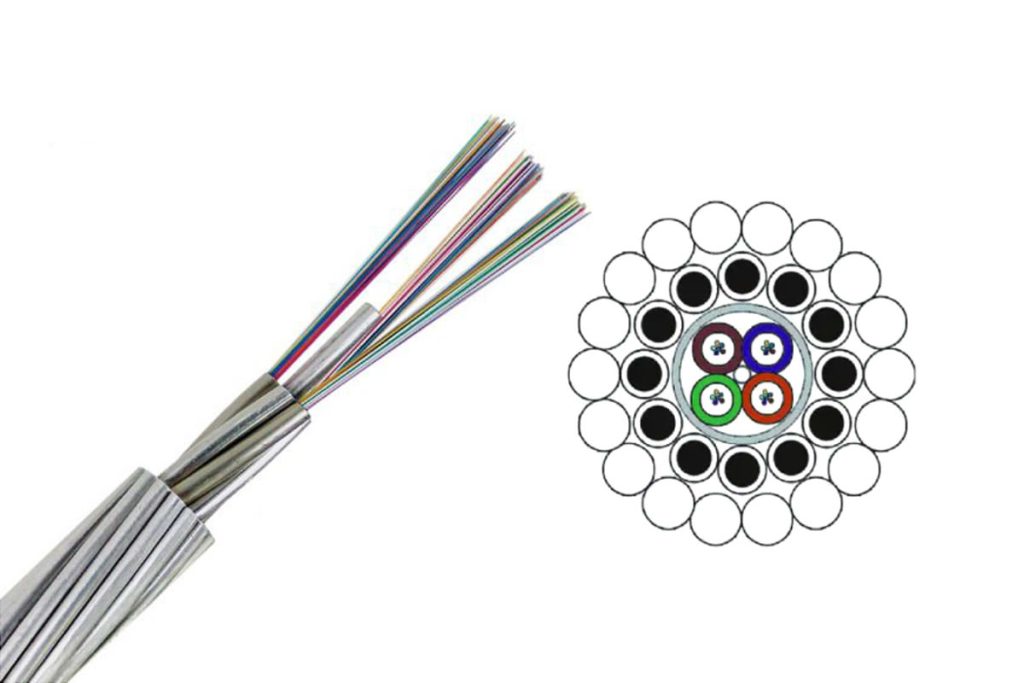

Learn more: ADSS OPGW OPPC: Selection of Fiber Optic in Air Lines
6.Submarine Optical Fiber:
- Used for underwater communication links, the underwater fiber optic cable Has specialized construction to withstand ocean conditions.
- Price range: about $10.00 a $500.00 per meter, o $10,000 a $500,000 per kilometer.
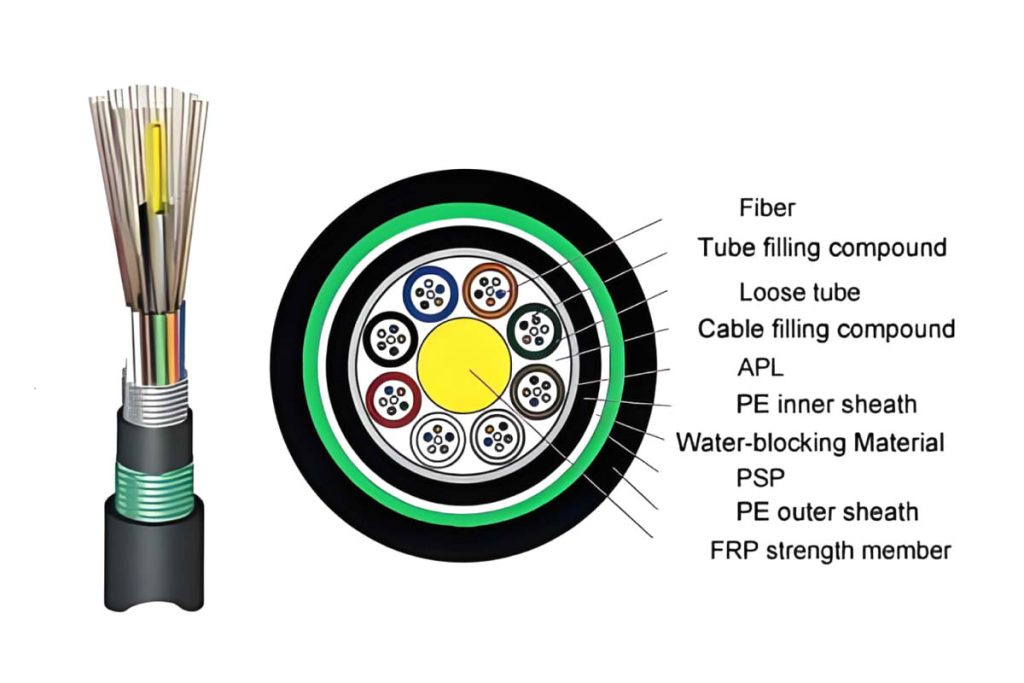
These prices reflect the cost of the fiber itself and do not include additional costs for installation, connectors, splices, testing and maintenance. Besides, high-end special fibers, as fibers insensitive to bending, radiation resistant fibers or fibers designed for specific environments, may have an additional cost.
It is important to note that prices may fluctuate in response to technological advances., production efficiencies and changes in market supply and demand. For example, The cost of optical fibers may increase during periods of global supply chain restrictions or increases in raw material prices. Therefore, for the most up-to-date pricing information, it is recommended consult with suppliers directly or review industry reports.
Composition and Manufacturing of Optical Fibers
Basic Structure: Core, Coating and Coating Materials and Functions
Fiber optic cables are made up of three main layers: the core, coating and coating. The nucleus, typically made of glass or ultra-pure plastic, It is the central part of the fiber where light signals are transmitted. Surrounding the core is the cladding, a layer of material with a lower refractive index that reflects light back to the core, minimizing signal loss and allowing data to travel long distances. The outermost layer, the coating, It is designed to protect the core and cladding from physical damage and environmental factors. This coating is usually made of polymeric materials that provide flexibility and durability, ensuring the fiber can withstand bending and handling during installation and use.
Fabrication process: Stretching Techniques, Coating Technology, Final Face Treatment
The manufacturing process of fiber optic cables involves several critical steps, each of which contributes to the overall quality and performance of the final product. Starts with the creation of the preform, a cylindrical piece of glass or plastic that serves as the source material for the fiber. The preform is heated to a high temperature and then stretched into a thin fiber., a process known as fiber drawing. During this step, Precise control is maintained to ensure that the fiber diameter remains constant and that the core and cladding layers are formed correctly.

After the stretching process, the fiber is coated with protective layers to improve its strength and flexibility. Advanced coating technologies are used to apply multiple layers of polymer coatings that protect the fiber from environmental and mechanical stresses. The final step in the manufacturing process is the final face treatment, where the ends of the fiber are polished and treated to ensure they can transmit light signals with minimal loss. This step is crucial to maintain the integrity of the data transmission, especially in high performance applications.
Technical Challenges and Cost Considerations: Material Purity, Production Efficiency, QA
The production of high quality optical fibers involves overcoming various technical challenges, each with associated cost considerations. The purity of the material is essential, since impurities in glass or plastic can significantly degrade fiber performance by causing signal attenuation. Achieving the required level of purity requires sophisticated manufacturing techniques and strict quality control measures., which can increase production costs.
Production efficiency is another critical factor, with manufacturers continually looking for ways to optimize drawing and coating processes to produce optical fibers faster and at lower costs. Nevertheless, These efforts must be balanced with the need to maintain high quality standards. Quality control is essential throughout the manufacturing process, from initial preform creation to final face treatment. Rigorous testing and inspections are performed to ensure each fiber meets required performance and durability specifications., which adds to the total production costs but ensures the reliability and longevity of the fiber optic cables.
Material Costs and Price Fluctuations
Raw Material Costs: Quartz, Polymers, etc.
The production of fiber optic cables is highly dependent on high-quality raw materials, mainly quartz and various polymers. The quartz, a form of silica, It is the fundamental component used to make the glass core and cladding of fiber optic cable. The purity of the quartz is crucial because even the smallest impurities can affect the performance of the fiber, causing increased signal loss and reduced transmission quality. As a result, Obtaining ultrapure quartz can be expensive, with prices that fluctuate depending on availability, mining processes and market demand. From 2024, The price of high purity quartz for the production of optical fiber can range between $100 Y $500 per kilogram.
Polymers are used to create the protective coatings for fiber optic cables. These coatings provide essential mechanical protection and environmental resistance, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the cables. The cost of polymers can vary depending on the type and quality required, as well as market conditions for petrochemical products. Basic polymer coatings can cost around $5 a $10 per kilogram, while advanced polymers offering enhanced performance characteristics, such as greater flexibility and durability, They can range between $20 Y $50 per kilogram. These high-end polymers contribute significantly to the total material costs in fiber optic production.
Production Costs: Energy Consumption, Labor Costs, Equipment Depreciation
Production costs are another important factor that influences the price of fiber optic cables.. The process of fiber optic cable manufacturing It is energy intensive, requiring high temperatures for fusion and stretching of quartz, as well as precise control during the coating and curing stages. Consequently, Fluctuations in energy prices can directly affect production costs, with higher energy costs leading to increased prices of the final product.
Labor costs also play a crucial role in fiber optic manufacturing. Skilled labor is needed to operate advanced machinery, Ensure quality control and manage the complex processes involved in creating high-performance optical fibers. Labor cost can vary significantly by region, with higher wages in developed countries leading to higher production costs compared to regions with lower labor costs.
Equipment depreciation is another important consideration. The machinery used in the manufacturing of fiber optics is highly specialized and, often, represents a significant capital investment. Over time, this equipment depreciates, and manufacturers must take these costs into account when setting prices for their products. Regular maintenance and upgrades to keep equipment running efficiently also contribute to total production costs..
Market Supply and Demand: Global Supply Chains, Price Indices, Forecast Analysis
The global dynamics of supply and demand for fiber optic cables significantly influence their price. On the supply side, factors such as availability of raw materials, production capacity and geopolitical events can affect the market. Disruptions in the supply chain, such as natural disasters or trade restrictions, can lead to shortages and price increases for raw materials and finished products.
On the demand side, the growing need for high speed internet, Advances in telecommunications and data center expansion drive demand for fiber optic cables. This increasing demand can lead to higher prices, especially if the offer cannot keep up. Market price indices for fiber optic materials and products provide valuable information on current trends and help manufacturers and consumers forecast future prices..
Regional Differences: Logistics Costs, Duty, Exchange Rate Impacts
Regional differences can also affect the price of fiber optic cables. Logistics costs, including transportation and storage, vary by region and can significantly impact the total cost of delivering fiber optic products to the market. Regions with higher transportation costs or more complex logistics networks may see higher prices for fiber optic cables.
Tariffs and trade policies also play a crucial role in regional price differences.. Import duties and trade restrictions can increase the cost of raw materials and finished products, leading to higher prices in regions affected by these policies. Fluctuations in exchange rates can further complicate pricing, as changes in currency values can affect the cost of importing and exporting goods.
Fiber Optic Communication Equipment Prices
Key Equipment Overview: Optical Transceivers, Switches, Amplifiers, Dividers
Fiber optic communication systems rely on various specialized equipment to function effectively.. Key components include optical transceivers, switches, amplifiers and dividers, each of which plays a vital role in ensuring smooth data transmission.
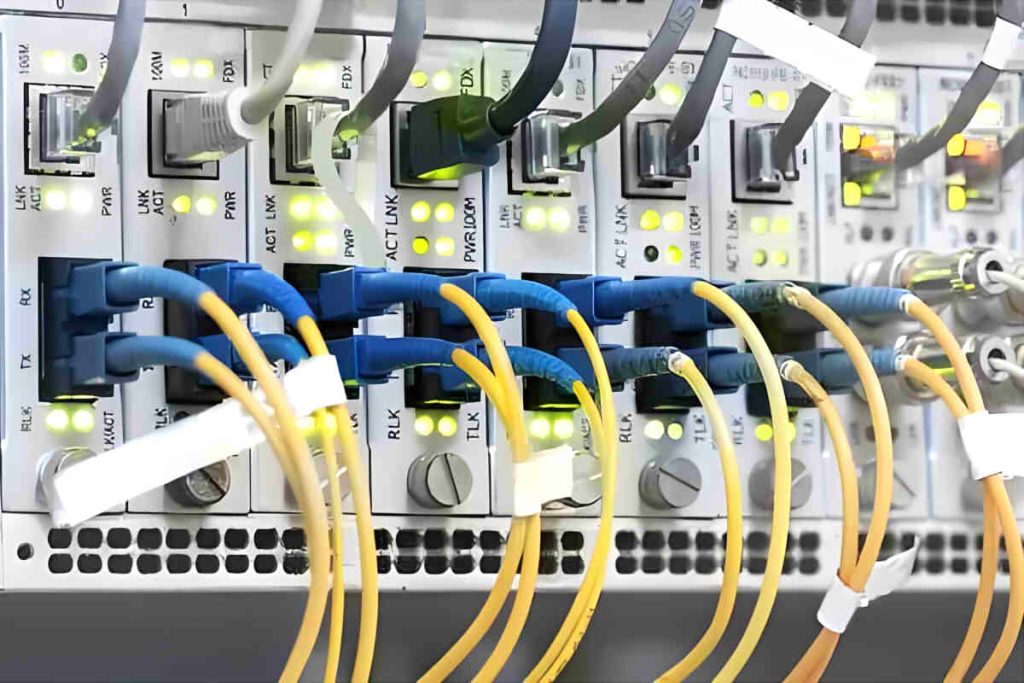

- Optical Transceivers: These devices convert electrical signals into optical signals and vice versa., allowing data transmission over fiber optic cables. The price of optical transceivers varies widely depending on factors such as transmission speed, distance capabilities and form factor. Basic transceivers can cost between $20 Y $50, while high-end models for long distance and high speed applications can range from $1,000 Y $3,000 or more.
- Switches: Optical switches are crucial for directing data traffic within a network. They come in various configurations, including basic unmanaged switches and advanced managed switches with multiple ports and enhanced features. Prices vary from $100 for simple models up to $10,000 or more for high-capacity, feature-rich switches.
- Amplifiers: Optical amplifiers increase the strength of optical signals to extend the range of fiber optic networks. They are essential for long distance communication links. The cost of optical amplifiers depends on the amplification technology used and the power levels required, typically oscillating between $500 Y $5,000 per unit.
- Dividers: Optical splitters split a single optical signal into multiple signals, allowing efficient distribution of data. The price of splitters varies depending on the number of output ports and the type of splitter, with costs ranging from $10 until $200 per unit.
Technological Advances and Cost Relationships: Integration, Modularity, Standardization
Technological advances significantly impact the price of fiber optic communication equipment. The integration, Modularity and standardization are key trends driving cost changes.
- Integration: As manufacturers pack more features into single devices, the overall cost of deploying fiber optic networks can decrease. Integrated transceivers and amplifiers, for example, reduce the need for multiple discrete components, simplifying installation and maintenance and, potentially, reducing costs.
- Modularity: Modular designs allow network operators to add or upgrade components as needed, offering flexibility and cost savings. Instead of replacing entire systems, operators can invest in specific modules, such as higher capacity switches or improved transceivers, what can be more profitable in the long term.
- Standardization: Industry standards help ensure compatibility between equipment from different manufacturers, encouraging competition and reducing prices. Standardized components, like SFP transceivers (Small Form-factor Pluggable), benefit from economies of scale, resulting in lower costs for end users.
Maintenance and Update Costs: Spare Parts Inventory, Technical Support, System Compatibility
The total cost of ownership of fiber optic communication equipment includes not only the initial purchase price, but also the ongoing maintenance and upgrade costs.
- Spare Parts Inventory: Maintaining an inventory of spare parts is essential to minimize downtime in the event of equipment failure. The cost of spare parts varies depending on the equipment and the manufacturer's pricing policies.. Network operators must balance the cost of holding inventory with the risk and expense of potential downtime.
- Technical Support: Access to technical support is crucial to addressing issues and ensuring smooth operation of fiber optic networks. Many equipment manufacturers offer support packages, which can range from basic assistance to full support plans. The cost of these plans varies, the most extensive plans being generally the ones with the highest rates.
- System Compatibility: Upgrading fiber optic equipment often involves ensuring compatibility with existing systems. Incompatible components can lead to additional expenses on adapters or even a complete system overhaul. Therefore, Choosing equipment that adheres to industry standards and offers backward compatibility can help reduce upgrade costs.
Understanding these factors allows network operators to make informed decisions to optimize their investments and manage costs effectively..
Example: Cost and Profitability Analysis for a Communication Service Provider

Cost Estimates
1. Fiber Optic Cable and Equipment Costs
- Assuming they are installed 100 kilometers of fiber, the cost per kilometer of fiber (including installation) It is $10,000, resulting in a total cost of $1,000,000.
- Network equipment costs, as optical transceivers, routers, switches, etc., others can add $500,000.
- Total initial cost: $1,500,000.
2. Installation and Placement Costs
- This includes trenching, filling, marked, evidence, etc. Assuming an installation cost of $2,000 per kilometer, the total cost would be $200,000.
3. Maintenance and Operation Costs
- Includes electricity, staff salaries, maintenance, fault repair, etc. Assuming an annual operating cost of 10% of total income.
4. Management and Marketing Costs
- Includes office facilities, human resources, advertising and promotions, etc., assuming an annual cost of 5% of gross income.
Income Estimate
Assuming the service provider plans to cover 10,000 homes and collect $50 per month per household per service, so:
- Annual Income: 10,000 homes * $50/mes * 12 months = $6,000,000/year.
Recovery Period Calculation
- Gross Income for the first year: $6,000,000
- Operational and Maintenance Costs: $600,000 (10% from $6,000,000)
- Management and Marketing Costs: $300,000 (5% from $6,000,000)
- Net Income for the first year: $6,000,000 – $900,000 = $5,100,000
- Initial Investment: $1,700,000 ($1,500,000 + $200,000)
- Residual Income in the first year: $5,100,000 – $1,700,000 = $3,400,000
Therefore, The investment will be recovered within the first year with an additional profit.
Precautions
- This is an extremely simplified model. In fact, It may take several years to fully recover the initial investment, especially if interest must be paid on loans or other financing costs.
- Costs and revenues can be affected by many factors, including competition, market demand, technological advances, government subsidies or tax policies.
- In practice, It is also necessary to consider the impact of factors such as market penetration, subscriber growth rate, service quality and customer satisfaction in revenue.
Although this model suggests a rapid recovery period within the first year, The actual payback period for large-scale fiber optic deployments can range from three to five years, particularly if the number of subscribers grows rapidly in the initial phase. The exact recovery period will depend on several factors, including the speed of subscriber acquisition and external economic conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding the price of fiber optics is crucial for both consumers and companies involved in the telecommunications industry.. The cost of fiber optic cables and related equipment is influenced by numerous factors, including raw material prices, manufacturing processes, market demand and technological advances. Besides, costs associated with installation, Maintenance and operation contribute significantly to the total investment required to deploy fiber optic networks.
Despite the high initial costs, the benefits of fiber optics—such as high-speed data transmission, reliability and scalability—make it an essential component of modern communication infrastructure. The example of a service provider investing in fiber optic infrastructure demonstrates that, with effective cost management and a strong customer base, recovery period may be relatively short, leading to substantial long-term profitability.
As technology continues to evolve and demand for high-speed internet and data services increases, Fiber Optic Cost Dynamics Likely to Change. Factors such as advances in manufacturing efficiency, Changes in commodity prices and regulatory policies will continue to shape the market.