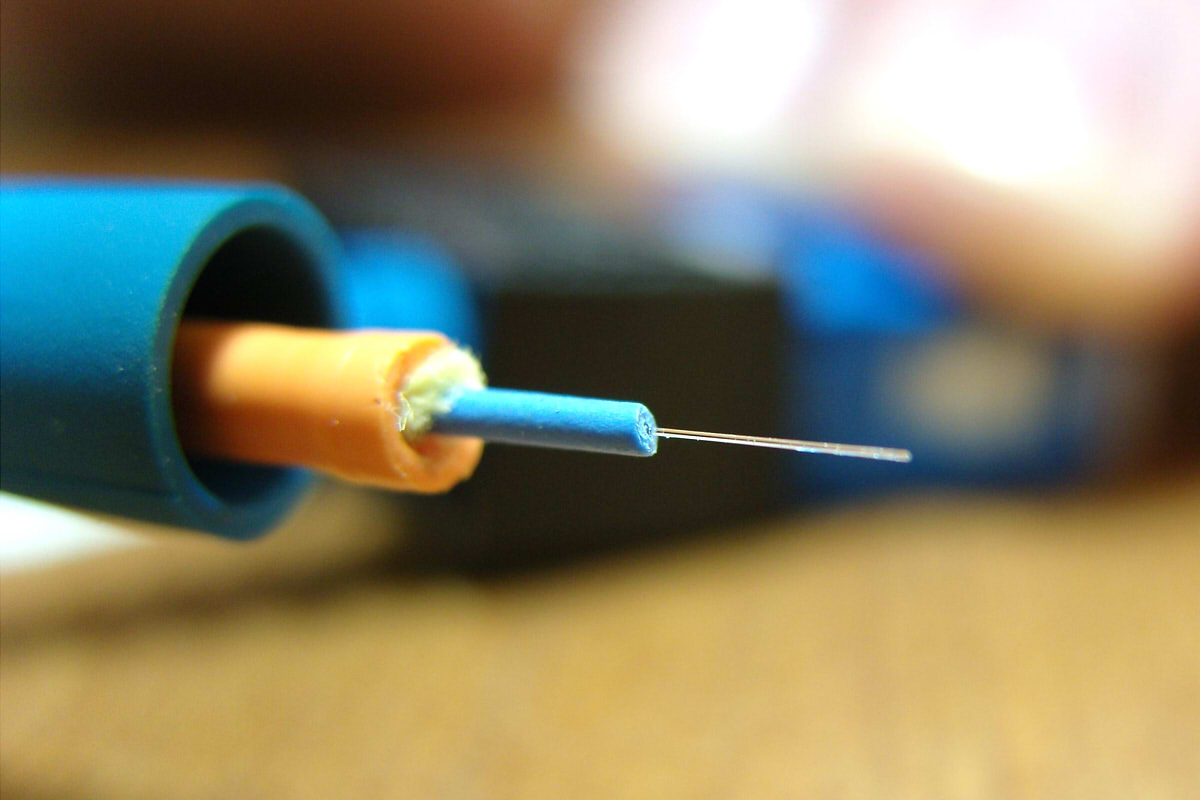
Fiber optics are the most basic and commonly used product in the field of communications.. Optical fiber can be divided into single-mode optical fiber and multimode optical fiber.. in a short sentence, single-mode optical fiber is suitable for long-distance communication transmission, while multimode optical fiber is suitable for short-distance communication transmission.
Table of Contents
- Singlemode Optical Fiber
- Multimode Fiber Optic
- Singlemode and Multimode Fiber Types
- Differences between Singlemode and Multimode Fiber Optic
- Frequent questions
- What type of fiber optic should I choose??
- Why is the transmission distance of multimode optical fiber not as long as that of single mode??
- Differences between multimode and singlemode fiber optic transceivers
- Can singlemode/multimode optical fibers be mixed with singlemode/multimode optical modules??
- How to choose the right fiber optic cable?
- How to decide between a fixed or detachable fiber optic connection?
- In fixed fiber optic connections, Should I choose mechanical joining or heat fusion??
Singlemode Optical Fiber
When the geometric dimensions of the optical fiber (mainly the core diameter) are close to the wavelength of light, as a core diameter d1 in the range of 5~10µm, Fiber optics only allow one mode propagation (basic mode HE11), with all other higher modes completely dimmed. The optical fiber that transmits in this way is called single-mode optical fiber..
The transmission rate of single-mode optical fiber is 100M/s or 1G/s, with a transmission distance of more than 5km. Generally, Single-mode optical fiber is used for long-distance signal transmission. Its light source is a laser light source, with applicable wavelengths of 1310nm/1550nm. The wire color is generally yellow, and the connectors are mostly blue or green.

Since it only has one mode of propagation, avoids the problem of modal dispersion, Thus, the single-mode optical fiber It has a very wide bandwidth, especially suitable for large capacity fiber optic communication. Therefore, to achieve single mode transmission, It is necessary that the parameters of the optical fiber meet certain conditions. For example, through formula calculations, for an optical fiber with NA=0.12 and to achieve single-mode transmission at wavelengths greater than λ=1.3µm, fiber core radius should be ≤4.2µm, namely, its core diameter d1 should be ≤8.4µm. Since the core diameter of single-mode fiber optic cable is very small, This places stricter requirements on your manufacturing process..
Multimode Fiber Optic
When the geometric dimensions of the optical fiber (mainly the core diameter d1) They are much longer than the wavelength of light, There may be dozens or even hundreds of propagation modes in optical fiber.. The optical fiber that transmits in this way is called multimode optical fiber..
The core of the multimode fiber optic cable is 50μm/62.5μm, with a typical rate of 100M/s, and the transmission distance can reach 2km, 1 G/s can reach 1000m, Y 10 G/s can reach 550m. Its light source is an LED light source, with applicable wavelengths of 850nm/1310nm. Gigabit cable color is mostly orange, and to 10 Gigabit is mostly aqua blue, with connectors mostly in gray white.
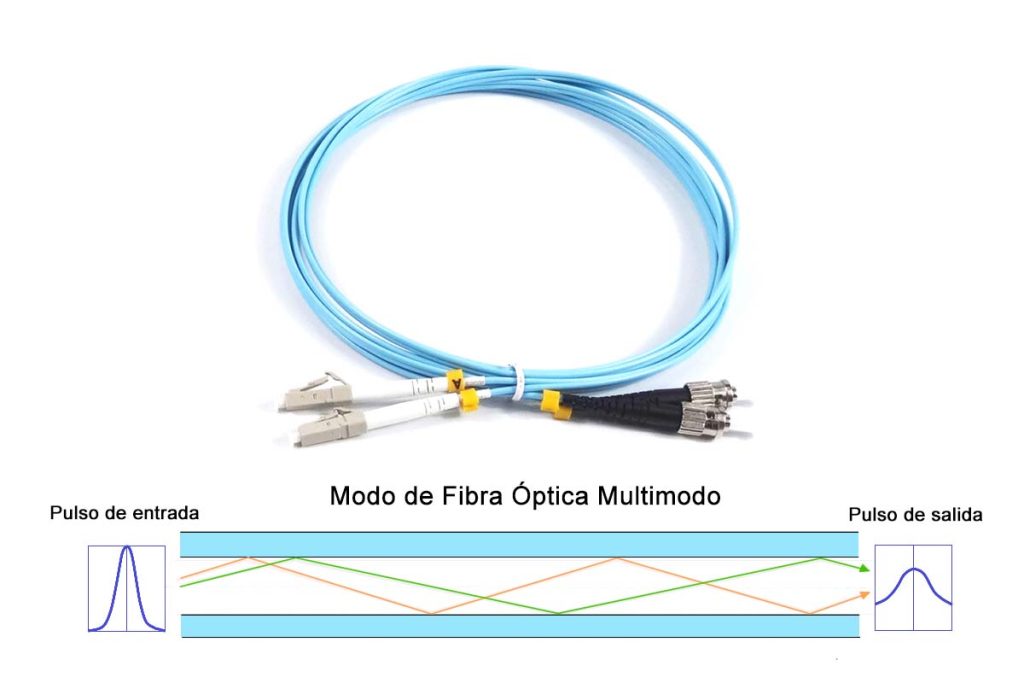

Because different propagation modes have different propagation speeds and phases, long distance transmission may result in delays and broadening of light pulses. This phenomenon is called modal dispersion of optical fiber. (also called intermodal dispersion). Modal dispersion causes the bandwidth of multimode optical fiber to narrow, reducing its transmission capacity, Thus, multimode optical fiber is only suitable for communication of fiber optic capacity smaller.
Singlemode and Multimode Fiber Types
Among the types of single-mode optical fiber are G652, G655 y G657. Secondly, Multimode optical fiber types include OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4 and OM5.
OM5 patch cables are usually lime green in color. Unlike OM4 patch cables, which only support the transmission of a single wavelength at a time, OM5s can support up to four wavelengths simultaneously and have a longer transmission distance. This makes them widely applicable to 40G/100G cabling infrastructure in data centers.. OM1/OM2 are widely used indoors and are generally orange in color. OM3/OM4 are usually aqua blue, but they are also available in purple and magenta, and are mainly used for 10G to 40G/100G cabling in data centers.
Differences between Singlemode and Multimode Fiber Optic
Core Diameter
The main difference between single-mode and multimode optical fiber is the core diameter.; the multimode has a larger diameter, typically of 50 o 62.5µm. While the typical core diameter of single-mode fiber is 8 y 10µm, both types have a coating diameter of 125µm.
Light source
Fiber optics generally use lasers or LEDs as the light source. laser light sources, which are significantly more expensive than LEDs, They generate light that can be precisely controlled and have high power. LEDs generate more dispersed light (many light modes), which is generally used for multimode fiber. Meanwhile, laser light sources (that generate light close to a single mode) They are generally used for single-mode fiber optics.
Bandwidth
Multimode optical fiber, with its larger core size, allows multiple transmission modes, resulting in modal dispersion and narrower bandwidth. This results in a higher pulse expansion rate, limiting the information transmission capacity of multimode fiber. Secondly, The modal dispersion in single-mode fiber is much lower than in multimode fiber., which gives it a much wider bandwidth, especially suitable for high capacity communications.
Coating Color
Coating color is sometimes used to distinguish between single-mode and multimode fiber optic patch cables.. According to the standard TIA-598C, in non-military applications, single-mode fiber uses a yellow outer coating, while multimode fiber uses an orange or aqua coating. Depending on the type, some manufacturers use other colors to differentiate high performance OM5 fiber from other fiber types.
Precio
Although multimode fiber can support multiple light modes and its price is higher than singlemode, Single-mode fiber devices generally use solid-state laser diodes, which are more expensive. While single-mode fiber modules can transmit up to 150-200 km, multimode fiber modules can only reach up to 2 km. Nevertheless, devices used in single-mode fiber modules are approximately twice as expensive as those in multimode fiber modules, so the cost of single-mode cable equipment is much higher than that of multimode cable.
Under short distance light transmission conditions, especially in local network cabling scenarios, multimode fiber works as well as singlemode. Therefore, driven by cost advantage, multimode fiber is more suitable for data center construction.
Frequent questions
What type of fiber optic should I choose??
The choice of fiber optics should be based on the transmission distance and total budget. If the distance is a few miles, multimode optical fiber will work well and the cost of the transmission system (senders and receivers) will vary between 500 Y 600 Dollars. If the transmission distance exceeds 6-10 kilometres, whether to opt for single-mode optical fiber, but due to the increase in cost of laser diodes, The cost of the transmission system will generally exceed the 1000 Dollars. For outdoor use, should be used armored fiber optic cables.

Why is the transmission distance of multimode optical fiber not as long as that of single mode??
Fiber optic operational wavelengths include the short wavelength of 850nm, as well as 1310nm and 1550nm. The loss in optical fiber generally decreases as the wavelength increases.. The loss at 850nm is 2.5dB/km, and multimode optical fiber operates at this wavelength, resulting in considerable loss. Secondly, The operating wavelengths for single-mode optical fiber are 1310nm with a loss of 0.35dB/km, and 1550nm with a loss of 0.20dB/km, What are the lowest losses in fiber optics?.
Differences between multimode and singlemode fiber optic transceivers
- Precio: Multimode fiber optic transceivers are cheaper, while single-mode fiber optics are more expensive.
- Distance: Multimode fiber optic transceivers are used for distances less than 2KM, while single-mode fiber optic transceivers can reach distances of more than 100KM.
In today's market, multimode transceivers are economical, with an approximate price of 40 enough dollars for 100Mbps bandwidth. Compared, single-mode transceivers are less common and more expensive, with an approximate price of 60 dollars and a bandwidth of 1000Mbps.
Can singlemode/multimode optical fibers be mixed with singlemode/multimode optical modules??
Single-mode and multimode optical fibers should not be mixed with single-mode and multimode optical modules., respectively. If transmitted with a single-mode module in multimode optical fiber, significant packet loss will occur. Besides, The large difference in core diameter between single-mode and multimode fiber will result in too high an insertion loss when trying to combine the two.. Multi-mode and single-mode converters must have corresponding wavelength and light transmission and reception functions to realize electro-optical conversion properly..
How to choose the right fiber optic cable?
Choosing fiber optic cable, in addition to being based on the number of fibers and the type of fiber, should consider the structure and outer sheath of the cable according to the use environment.
- For outdoor use and direct burial, It is recommended to choose loosely armored fiber optic cables. For aerial laying, can be chosen loose fiber optic aerial cables with one or more reinforcing rods and black PE outer cover.
- Fiber optic cables used inside buildings should be tight type and pay attention to their fire resistance characteristics. Generally, in ducts or places with forced ventilation, smoke fire resistant types can be chosen (Plenum) or non-toxic combustible types (LSZH), while in exposed environments a fire resistant type should be chosen, non-toxic and smokeless.
- For vertical or horizontal wiring within buildings, tight fiber optic cables can be chosen, distribution cables or branch cables that are common indoors.
- Depending on the network application and cable application parameters, choose between singlemode and multimode optical fiber; generally, For indoor and short-distance applications, multimode fiber is preferred., while for outdoor and long-distance applications, single-mode fiber is preferred..

How to decide between a fixed or detachable fiber optic connection?
The detachable fiber optic connection is achieved through fiber optic connectors. An active connection point in the fiber link chain is a clear separation interface. When choosing between fixed and removable connections, Fixed connections have the advantage of lower cost and light loss, but they are less flexible, while detachable connections are the opposite.
In network design, should be flexibly chosen between the use of fixed and detachable connections according to the complete situation of the link chain, ensuring flexibility and stability, and taking advantage of the advantages of each. Detachable connection interface is a critical point for testing, maintenance and changes, making it easier to locate faults in the link chain and replace faulty components, thereby improving system maintainability and reducing maintenance costs.
In fixed fiber optic connections, Should I choose mechanical joining or heat fusion??
The mechanical union, also known as fiber optic cold splicing, does not require a fusion splicing machine and uses mechanical connection techniques to make a permanent union of one or more optical fibers. Usually, for connecting a small number of fibers at multiple dispersed locations, mechanical joining is preferred over fusion splicing.
The mechanical joining technique has been widely used in emergency line repairs., small scale applications in special situations and other engineering practices. With the massive deployment of fiber to the desktop and fiber to the home (FTTH) in recent years, Mechanical joining has been recognized as an important means of fiber optic connection.
For fiber to the desktop and fiber to the home applications, which are characterized by having a large number of geographically dispersed users, when the user scale reaches a certain level, the complexity of construction and the availability of personnel and fusion splicing equipment cannot meet the times required for user service. Due to its simple operation, short staff training period and low investment in equipment, Mechanical splicing offers the most cost-effective fiber optic connection solution for large-scale deployments.
Secondly, the fiber optic splicing due to fusion requires greater training for personnel and more advanced equipment, and must be used on trunk communication routes to ensure the safety and reliability of the line.