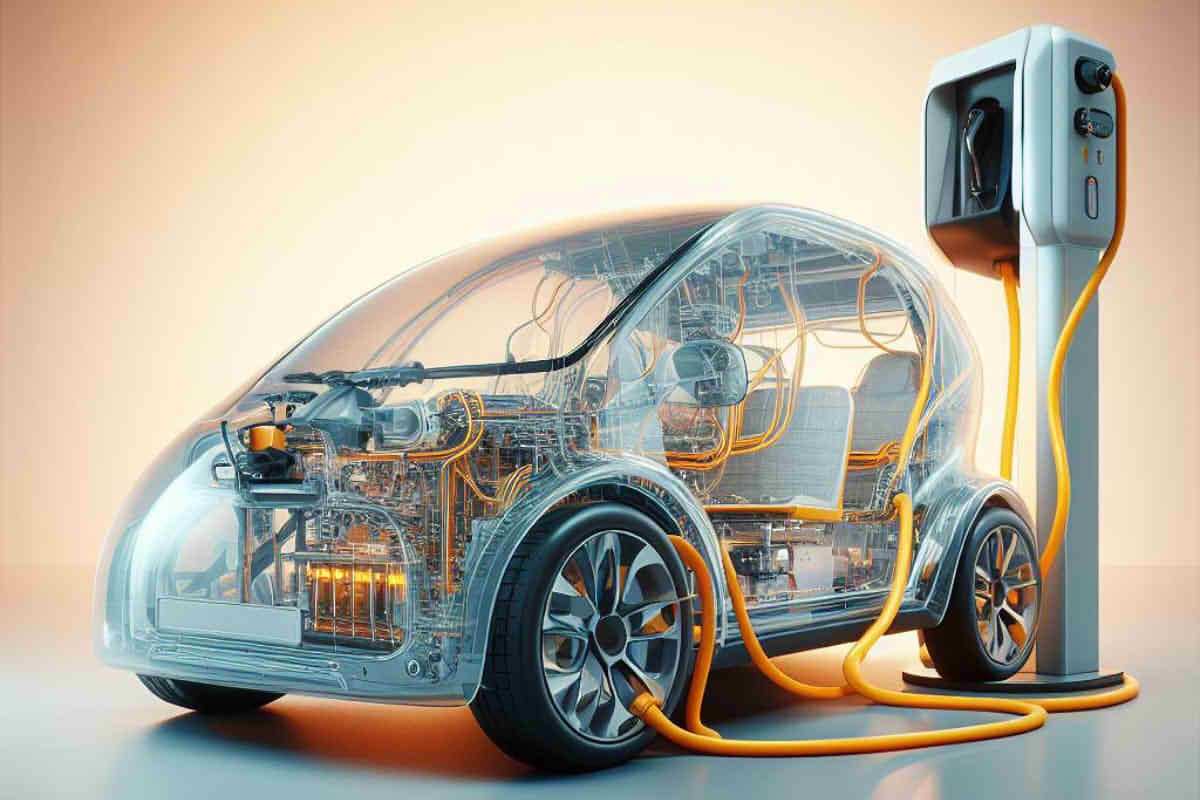
Electric vehicles are experiencing an unprecedented boom around the world. According to Statista projections, for 2028 The electric vehicle market is expected to reach 17.07 million units, with an estimated market value of $906.7 billion. This exponential growth is accompanied by increasing demand for specialized electric vehicle cables designed to meet the unique challenges that electric vehicles present compared to internal combustion cars..
Table of Contents
- Application and Performance of Specialized Cables for Electric Vehicles
- High Voltage Wiring Inside Electric Vehicles
- Selection and Requirements of Specialized Cables for Electric Vehicles
- Conclusion
Application and Performance of Specialized Cables for Electric Vehicles
Los specialized cables for electric vehicles are divided into two main categories: single core and multicore. The main difference between these cables and those used in internal combustion vehicles lies in the environment in which they are used..
High Voltage and Current
One of the most significant challenges that electric vehicle cables face is the high voltage and current they must withstand.. While traditional vehicles operate with 12V batteries, Electric vehicles can reach voltages as high as 600/300A, requiring cables with much higher voltage ratings.
Large Diameter and Large Quantity of Cables
Electric vehicles contain a variety of components, as high voltage inverters, transformers, low voltage batteries, air conditioning compressors, electric heating systems and power distribution units, all connected by cables. This component density results in a large number of cables in a limited space.
Exposure to the Environment
Los electric vehicle charging gun cables are exposed for long periods of time, which requires strict requirements for resistance to climatic conditions, abrasion, bending and tearing.
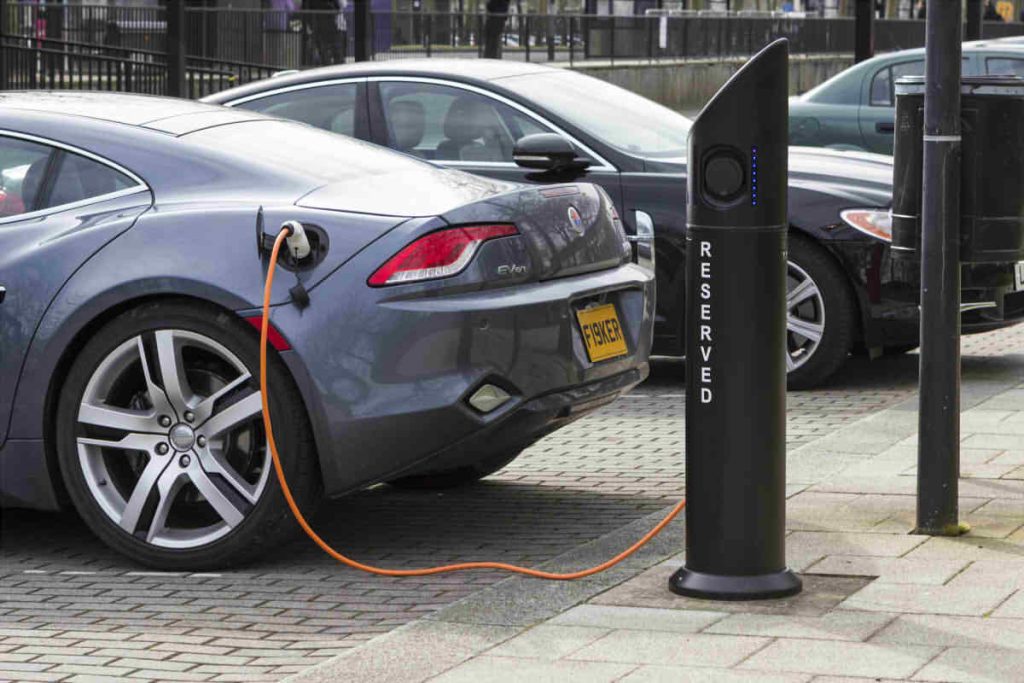

High Voltage Wiring Inside Electric Vehicles
High voltage wire harnesses inside electric vehicles are characterized by high voltage, high current and large number of large diameter conductors. Your design faces challenges related to routing, safety, the shielding, weight and cost.
Routing
Requirements for routing high voltage wire harnesses in a vehicle include:
- A minimum turning radius of 4 times the outer diameter of the cable for static loads.
- For dynamic loads, a minimum turning radius of 8 times the outer diameter of the cable.
- A minimum space of not less than 100 mm between high and low voltage conductors.
- The distance from the output end of the high voltage connector to the first fixed point must not exceed 100 mm.
- The distance between adjacent fixed points should generally not exceed 150-200 mm.
- The harnesses of high voltage cables should be placed under the vehicle as much as possible.
- Selection of heavy duty cables, like silicone cables, flexible cross-linked polyolefin cables.
Security
Since special cables for electric vehicles must carry high voltage and high current, The choice of cables must consider not only the insulation necessary for high voltage, but also the high temperature generated by the current. Internal high voltage cables must have excellent flame retardancy properties. Besides, require electromagnetic shielding to prevent electromagnetic interference from high voltage and large AC currents to electrical components and electronic devices.

Weight and Cost
In the case of electric vehicles, Weight reduction is essential to improve autonomy. Therefore, The aim is to minimize the weight of cable harnesses through the selection of appropriate materials. This includes the choice of aluminum conductors and low-density insulation materials with thin-wall processing.
Eco-Friendly
High-voltage wire harnesses in electric vehicles should be made from low-volatility materials, low VOC (volatile organic compounds) and low odor.
Selection and Requirements of Specialized Cables for Electric Vehicles
Cables for electric vehicles must meet a number of specific requirements, as resistance to high and low temperatures, oil and water resistance, flame retardancy, tensile strength and UV radiation resistance. Common materials include TPE, TPU, XLPO, NBR+PVC, neoprene rubber and silicone rubber.
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)
The TPE (thermoplastic elastomers), also known as thermoplastic rubber, are used in electric vehicle charging gun cables. They have advantages such as simple processing, low density and moderate price. The cables are very flexible and comply with existing standards. Nevertheless, They have disadvantages such as low resistance to high temperatures and poor resistance to oil and weather conditions..
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane Elastomer)
the tpu (elastomer thermoplastic polyurethane) It is used in the cables of electric vehicle charging stations. This material offers excellent tensile strength, strength and durability, in addition to being environmentally friendly. Nevertheless, can be more difficult to process and has a higher cost.
PVC (Chlorinated Polyurethane) Elastomer
pvc (chlorinated polyurethane) It is used in electric vehicle charging cables and is characterized by its fire resistance, isolation, resistance to acids and oils, ease of processing and affordable cost. Nevertheless, produces black smoke and hydrogen chloride gas when burned.
Silicone rubber
Silicone rubber cables are known for their heat resistance, to the cold, to climatic conditions, its impermeability and flexibility. They are suitable for a wide range of temperatures and harsh environments. Nevertheless, They are not oil resistant and can be more expensive.
XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene)
The XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene) offers greater flexibility and good electrical insulation for cables at a light weight and reasonable cost. Nevertheless, Its heat resistance is limited and it may have difficulty controlling color differences between batches..
Conclusion
Specialized cables for electric vehicles are essential components that face unique challenges due to high voltage, high current and exposure conditions. Advances in materials technology, as TPE, TPU, PVC, silicone and XLPE, are making it possible to address these challenges and contribute to the continued success of the electric vehicle industry.. As the electric vehicle market continues to grow at an impressive rate, Innovation in specialized cables is essential to promote electric mobility towards a more sustainable and efficient future.