There are many models of fiber optic cables, and the materials, structures and uses vary between them. To facilitate differentiation and use, A unified code has been established for fiber optic cables. This article will delve into the interpretation of this code to help you select the correct type of fiber optic cable..
Generally, The code of a fiber optic cable is made up of six parts: classification, reinforcing elements, structural characteristics of the cable, protective coating, outer layer and optical fibers.
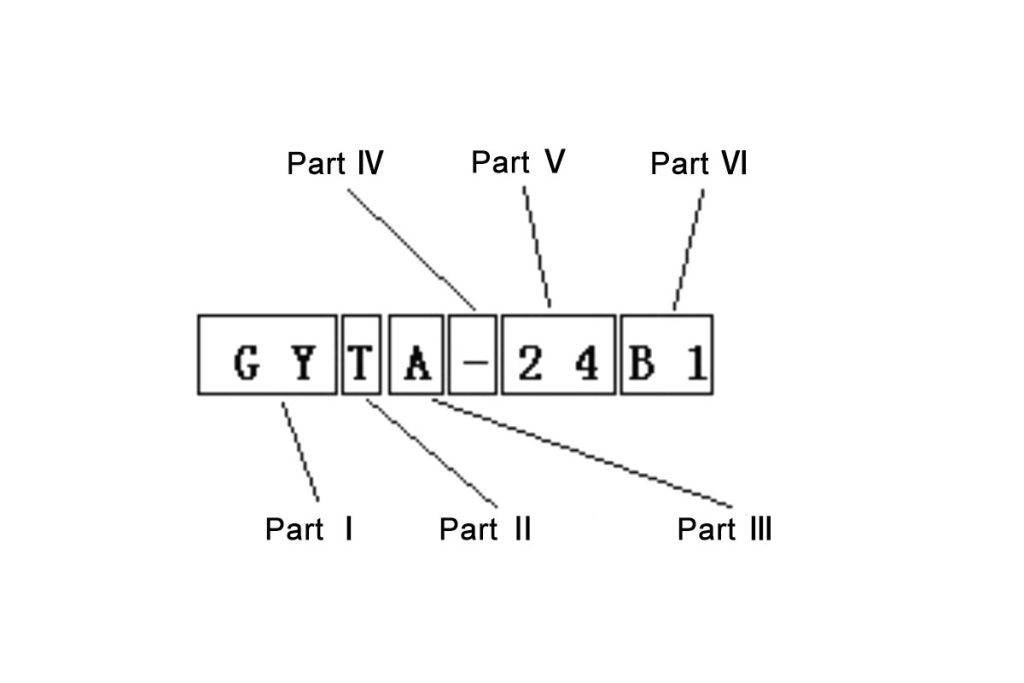
First part: Types of fiber optics
| Prefix | Use | Features |
|---|---|---|
| GY | Exterior for communications (campo) | Heavy, pressure and corrosion resistant, suitable for interconnection between external buildings and remote networks, long distance. |
| GJ | Interior for communications (local) | Flexible, bend resistant, fire resistant, suitable for indoor communication equipment, short distances. |
| GH | Submarine communications cable | No need for trenches or supports, lower investment and quick construction, less affected by the environment and human activities, high security and stability, mainly used for long distance international transmissions. |
| GT | Special communications cable | Includes fibers with dispersion displacement, non-zero dispersion, flat dispersion fibers, etc., for special uses in addition to other types. |
| GS | Interior for communications equipment | Uses heavy metal reinforcement components and loose fiber optic cladding structures, suitable for internal equipment. |
| MG | For coal mines | Adds retardant and anti-rodent properties, suitable for coal mines, gold mines, iron mines, etc. |
| GW | No metal for communications | Made of non-metal materials, Mainly used in areas with strong electromagnetic interference and frequent thunderstorms. |
| GR | Soft communications cable | small diameter, flexible, easy to fold, suitable for indoors or small spaces, used in fiber optic connectors, FTTH, sensors, etc. |
Between the first and second part: Reinforcement core
The reinforcement core reinforces the fiber optic cable with three different materials: metal, non-metal and heavy metal, improving the tensile strength and mechanical properties of the cable.
| Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| Sin | Metal reinforcement component |
| F | Non-metallic reinforcing component |
| G | Metal Heavy Reinforcement Component |
For example:
GYTA fiber optics: metal reinforcement core
GYFTA fiber optic: non-metallic reinforcement core
Second part: Structural features
The structural characteristics of the fiber optic cable should show the main type of the cable core and the derived structure of the fiber optic cable. When there are several structural characteristics for a type of fiber optic cable, combination codes can be used to represent them.

| Prefix | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| D | Fiber optic ribbon structure | Place fiber optic units in a large sleeve. Compact, high use of space, capable of hosting many optical fibers, complete splices of each unit. |
| Sin | Layered twist structure | Uses bi-directional torsion technology, completely waterproofs the cross section, fiber optic loss approaches zero, excellent environmental performance. Suitable for long distance communications, interlocal communications and environments with high requirements for resistance to moisture and rodents. |
| S | Fiber Optic Loose Cladding Structure | Several optical fibers are freely filled inside the tube, composed of several optical fibers, fiber optic cable gel and PBT coating layer. Mainly used for outdoor laying. |
| J | Fiber Optic Tight Cladding Structure | Composed of optical fibers and a PVC layer on the surface, forming a tight fiber, flexible and easy to peel. Generally used for indoor fiber optic cables or special fiber optic cables. |
| X | Center tube structure | Use loose tube as cable core, with the reinforcing components of the fiber optic cable around the loose tube. Small diameter, light, easy to lay. |
| G | skeleton structure | You can extract the necessary optical fibers and connect them with access fiber optic cables, It has good resistance to lateral pressure and can protect optical fibers well. |
| B | flat structure | Cable plano, the cable core adopts a flexible structure, ensuring the cable flexibility, thin relative thickness, small volume, simple connection, convenient disassembly, suitable for data or power transmission in electrical equipment. |
| T | Filling structure | Fill the inside of the optical fiber to maintain a circular shape, acting as fire protection, waterproofing, compression resistance, etc. |
| Z | Fireproof structure | Slows the spread of fire along the cable. Low cost, can avoid major disasters caused by delayed burning of cables, improving the level of line fire resistance |
| C | Self-supporting structure | Low fiber transmission loss, low dispersion, non-metallic structure, light, easy installation, strong resistance to electromagnetic interference, excellent mechanical and environmental performance, suitable for high voltage transmission lines. |
Third part: Lining material
Sheath material protects the cable core from mechanical action and environmental conditions.
| Prefix | Material |
|---|---|
| L | Aluminum |
| G | Steel |
| Q | Lead |
| Y | polyethylene coating |
| W | Steel-Polyethylene coating |
| A | Aluminum-Polyethylene coating |
| S | Steel-Polyethylene coating |
| V | Polyvinyl chloride coating (PVC) |
| F | Fluoroplastic |
| U | Polyurethane |
| E | Polyester elastomer |
Fourth and fifth part: Armor layer and covering layer
The fourth and fifth parts consist of two groups of numbers. The first group represents the armor layer, which can be a one or two digit number. The second group represents the coating layer, which is a single number.

armor layer
| Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Without armor |
| 2 | Double steel tape |
| 3 | thin steel wire |
| 4 | thick steel wire |
| 5 | corrugated steel tape |
| 6 | Double layer of steel wire |
| 23 | Polyethylene wound steel tape armor |
| 33 | Fine steel wire armor wound with polyethylene |
| 53 | Polyethylene Coated Corrugated Steel Tape Armor |
| 333 | Double layer armor of fine steel wire wound with polyethylene coating |
| 44 | Double layer thick steel wire |
Covering layer
| Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | fiberglass jacket |
| 2 | polyvinyl chloride jacket (PVC) |
| 3 | polyethylene jacket |
| 4 | Polyethylene jacket with nylon coating |
| 5 | polyethylene tube |
part six: Fiber Optic Cable Specifications
| Prefix | Description |
|---|---|
| A | multimode fiber |
| B | Singlemode fiber |
Applications of fiber optic cable models
To better understand fiber optic cable models, here are specific applications of common models:
| Name | Model | Structural features | Installation method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Center tube cable | GYXTY | Exterior, metal reinforcement core, tube central, full filling, polyethylene liner with steel wire reinforcement | aerial, buried |
| Center tube cable | GYXTS | Exterior, metal reinforcement core, tube central, full filling, steel-polyethylene coating | aerial, buried |
| Layered Braided Cable | WITH | Exterior, metal reinforcement core, layer braiding, full filling, aluminum-polyethylene coating | aerial, in tubes |
| Layered Braided Cable | GYTS | Exterior, metal reinforcement core, layer braiding, full filling, steel-polyethylene coating | aerial, in tubes, can also be buried |
| Layered Braided Cable | GYTA53 | Exterior, metal reinforcement core, layer braiding, full filling, aluminum-polyethylene skin with corrugated polyethylene steel outer skin | Buried |
| Layered Braided Cable | GYTY53 | Exterior, metal reinforcement core, layer braiding, full filling, polyethylene liner with corrugated steel outer liner | Buried |
| Cable sin metal | LTD | Exterior, non-metallic reinforcement core, fiber optic ribbon structure, full filling, polyethylene coating | aerial, high voltage induction areas |
| Cable sin metal | LTD03 | Exterior, non-metallic reinforcement core, layer braiding, full filling, no armor, polyethylene coating | aerial, ditch, high voltage induction areas |
| Cable sin metal | TOGETHER | Exterior, non-metallic reinforcement core, layer braiding, full filling, self-healing polyethylene liner | Hanging from high voltage pylons |
| Cable interior | GJFJV | Indoor use, non-metallic reinforcement core, tight fiber, polyethylene coating | Indoor or jump fiber connection |
| Cable interior | GJFJZY | Indoor use, non-metallic reinforcement core, tight fiber, fire resistant polyethylene coating | Indoor or jump fiber connection |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Understanding the fiber optic cable classification code is essential to selecting the suitable type of cable for specific applications. With this knowledge, Users can quickly identify the key features of each cable and determine which one best suits their particular needs in terms of installation environment, mechanical strength, environmental protection and transmission performance.
By understanding the different parts that make up the classification code, from fiber type and cable structure to cladding materials and technical specifications, Users can make informed decisions that optimize the efficiency and reliability of their optical communication networks.