In the age of electricity, high voltage cables are an essential part of our modern infrastructure. These cables carry large amounts of electrical energy over long distances., feeding our houses, industries and cities. Nevertheless, there has been persistent concern about whether radiation from these high voltage cables can affect human health. To fully understand this topic, First we must distinguish between two types of radiation: the ionizing and the electromagnetic.
Table of Contents
- Ionizing radiation
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Where is the Danger of High Voltage Cables?
- The Mystery of Crackling and Sparks in High Voltage Wires
- Conclusion
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation that carries enough energy to release electrons in atoms or molecules of a substance., ionizing these atoms or molecules.
Sources of Ionizing Radiation
The sources of ionizing radiation are varied, and can be of natural or human origin. Natural sources include cosmic radiation arriving from space, Earth's radiation emanating from radioactive minerals in the Earth's crust and radiation from radon gas released from the ground. These natural sources of radiation are a constant part of our environment and, usually, represent a relatively low risk to human health.

Secondly, Artificial sources of ionizing radiation are created by human activity and are often associated with medical applications, industrial and military. Artificial sources include radiotherapy machines used to treat cancer, nuclear reactors used to generate electrical energy and radioactive material used in industrial and scientific applications. These artificial sources can be much more intense than natural sources and, Thus, have a greater potential to cause harm.
Effects on the Human Body
When ionizing radiation interacts with the human body, can have harmful effects on cells and tissues. The main mechanism behind this is the ability of ionizing radiation to release electrons from atoms and molecules as it passes through them.. This process, known as ionization, can damage the genetic material of cells, cause breaks in DNA strands and increase the risk of mutations.
The effects of exposure to ionizing radiation depend on several factors., including the amount of radiation absorbed (dose), the type of radiation, the duration of exposure and the body part exposed. The effects can be acute, manifesting shortly after exposure, or chronic, developing over time. Symptoms of acute exposure may include nausea, vomiting, fatigue and damage to internal organs. Secondly, Chronic exposure can increase the risk of cancer and cause hematological disorders, like leukemia.
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is the transmission of energy and momentum in the form of waves in space., caused by electric and magnetic fields oscillating in the same direction and perpendicular to each other, that propagate in a direction perpendicular to the plane formed by the electric and magnetic fields.
The changing interaction between electric and magnetic fields generates electromagnetic waves, that are emitted into the air or spread, creating electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation has electric field and magnetic field components that oscillate in mutually perpendicular directions, transporting energy.
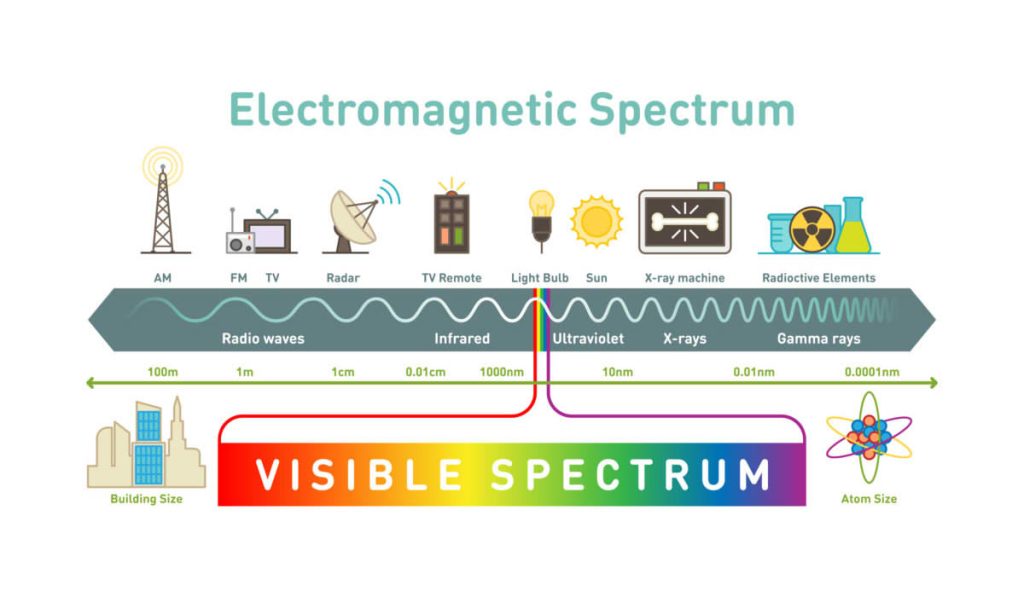
Electromagnetic radiation is classified into different types depending on its frequency or wavelength., including (from lowest to highest frequency): electric power, radio waves, microwave, terahertz radiation, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, x-rays and gamma rays. Among them, radio waves have the longest wavelength, while gamma rays have the shortest. X-rays and gamma rays have a high ionization capacity, while other types of electromagnetic radiation have a relatively low ionization capacity. Lower frequencies do not have ionization capacity.
Some forms of electromagnetic radiation have effects on the human body. Nevertheless, electromagnetic radiation requires a necessary condition for its generation: there must be a source of change over time, and the frequency of this switching source must be high enough to produce obvious radiation effects, usually above 3000 Hz.
The frequency of conventional alternating current is only 50 Hz, which is well below this value. Therefore, Electrical installations such as high voltage lines and substations do not generate electromagnetic radiation as mentioned..
Where is the Danger of High Voltage Cables?
The key to understanding the safety of high-voltage cables is that they do not emit ionizing radiation or electromagnetic radiation in the traditional sense.. Instead, generate very low frequency electromagnetic fields, also known as electric fields and induce magnetic fields. When the human body is in this electromagnetic field environment, an electric current is induced in the body, and it is important to control this induced current.
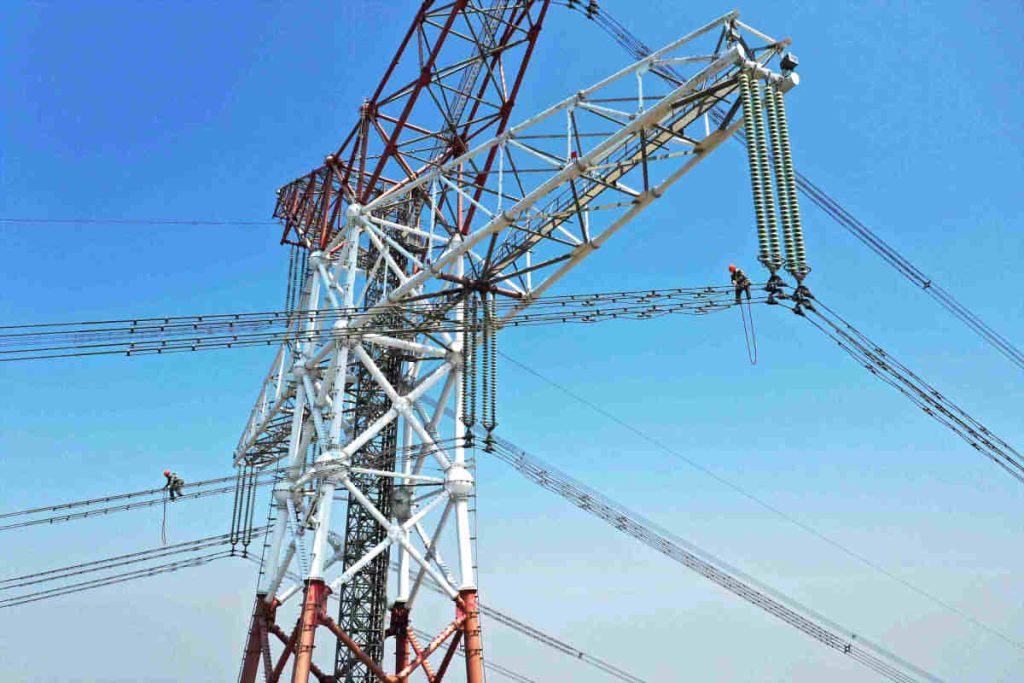

The main way to control the induced current is to maintain a safe distance from high voltage cables. According to the tests, outside the safety distance of the electrical installations of 220 kV, The intensity of the electromagnetic field is lower than that of common household appliances. Therefore, under normal conditions, there is no cause for concern. Besides, electrical installations, including the high voltage overhead cables, They are designed and built to meet strict safety standards, and generally there are signs that indicate the safety distance.
The Mystery of Crackling and Sparks in High Voltage Wires
When we look at high voltage cables, We often notice flashes and sparks accompanied by a characteristic sound, what is sometimes called “chisporroteo”. These phenomena are professionally known as corona discharge.. They occur due to the high intensity of the electric field on the surface of the overhead cable conductor, which causes the ionization of air and the release of electrons. As a result, the characteristic sizzling sound is heard, the smell of ozone is perceived and, especially at night, blue-violet flashes can be seen around the driver.

Corona discharge can have consequences, as loss of electrical energy, radio interference and audible noise. Nevertheless, It is important to note that corona discharge does not produce high frequency radiation and, Thus, does not pose a risk to human health. The only real annoyance it can cause is the noise., that can affect the rest of people in the vicinity. This is most evident in ultra high voltage lines and substations., but generally there are few people near these places.
Conclusion
In summary, It is essential to understand the difference between ionizing radiation and electromagnetic radiation when dealing with high voltage cables:
- ionizing radiation, from medical and industrial sources, It is dangerous to human health and can have serious effects, as seen in the Chernobyl and Fukushima incidents.
- High voltage cables operate at very low frequencies and do not emit electromagnetic radiation in the traditional sense and do not pose a risk to human health..
- Power frequency electromagnetic fields generated by tension cables high are very low intensity outside the safety distance, and its effect on the human body is practically insignificant.
- Sizzling and sparking observed in high voltage cables, known as corona discharge, They are normal phenomena and do not represent a danger to human health., apart from the possible noise they generate.
As a last resort, High voltage cables play an essential role in our electrical infrastructure and, when handled correctly, do not pose a significant risk to human health. Therefore, we can be sure that the electricity that powers our lives is essentially safe when it comes to radiation.

